GeoJSON
GeoJSON is a geospatial data interchange format based on JavaScript Object Notation (JSON). It defines several types of JSON objects and the manner in which they are combined to represent data about geographic features, their properties, and their spatial extents. GeoJSON uses a geographic coordinate reference system, World Geodetic System 1984, and units of decimal degrees.
Table of Contents
An Example
A GeoJSON Feature Collection looks like this:
{
"type": "FeatureCollection",
"features": [{
"type": "Feature",
"geometry": {
"type": "Point",
"coordinates": [102.0, 0.5]
},
"properties": {
"prop0": "value0"
}
}, {
"type": "Feature",
"geometry": {
"type": "LineString",
"coordinates": [
[102.0, 0.0],
[103.0, 1.0],
[104.0, 0.0],
[105.0, 1.0]
]
},
"properties": {
"prop0": "value0",
"prop1": 0.0
}
}, {
"type": "Feature",
"geometry": {
"type": "Polygon",
"coordinates": [
[
[100.0, 0.0],
[101.0, 0.0],
[101.0, 1.0],
[100.0, 1.0],
[100.0, 0.0]
]
]
},
"properties": {
"prop0": "value0",
"prop1": {
"this": "that"
}
}
}]
}
GeoJSON Objects Overview
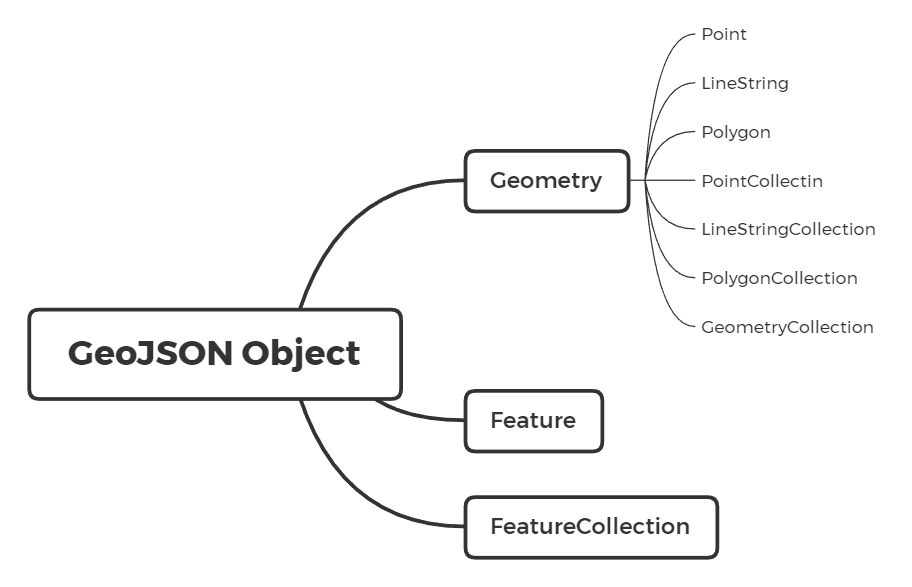
A GeoJSON object have 3 types:
- Geometry: A region of space
- Feature: A spatially bounded entity, which contains a Geometry object and additional properties. (append more properties to geometry!)
- FeatureCollection: A list of features
The GeoJSON object Geometry includes 7 types:
- Point: 0-dimentional point
- LineString: 1-dimentional curve
- Polygon: 2-dimentional surface
- MultiPoint: collection of Point
- MultiLineString: collection of LineString
- MultiPolygon: collection of Polygon
- GeometryCollection: collection of all the other types
Notes:
- Point, LineString and Polygon are the most fundamental objects. All the other Geometry objects, even all types of GeoJSON objects, are based on them.
- The types above are case-sensitive
- The “features” and “geometries” members, respectively, of these collection objects are standard ordered JSON arrays, not unordered sets.
Geometry
Geometries Except GeometryCollection
A Geometry (except GeometryCollection) consists of two parts: type and coordinates.
{
"type": "Point",
"coordinates": [102.0, 0.5]
}
The value of type property can be choosen from the 7 geometry types we talked above.
The format of the value of coordinates property differs.
Here are some definitions help to understand the following table:
- position:
- position of a point is an array of numbers.
- The first two elements are longitude and latitude, or easting and northing, precisely in that order and using decimal numbers. Altitude or elevation may be included as an optional third element:
[longitude/easting, latitude/northing, ?altitude/elevation]
- linear ring:
- A linear ring is the boundary of a surface(exterior ring) or the boundary of a hole(interior ring) in a surface.
- A linear ring is a closed LineString with four or more positions and its first and last positions are fully equivalent.
- A linear ring MUST follow the right-hand rule with respect to the area it bounds, i.e., exterior rings are counterclockwise, and holes are clockwise.
| Geometryg | coordinates Format | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Point | a single position | [103.0 31.0] |
| MultiPoint | an array of positions | [ [103.0, 31.0] ] |
| LineString | an array of two or more positions | [ [103.0, 31.0], [104.0, 31.0] ] |
| MultiLineString | an array of LineString coordinate arrays | [ [[103.0, 31.0], [104.0, 31.0]] ] |
| Polygon | an array of linear ring coordinate arrays (the first must be the exterior ring: [exterior, ...interiors]) |
[ [[102.0, 31.0], [103.0, 31.0], [104.0, 31.0]] ] |
| MultiPolygon | an array of Polygon coordinates | [ [[[102.0, 31.0], [103.0, 31.0], [104.0, 31.0]]]] ] |
GeometryCollection
Compared with the other geometries, GeometryCollection do not have the coordiantes member and have a new member called geometries instead. It looks like this:
{
"type": "GeometryCollection",
"geometries": [
{
"type": "Point",
"coordinates": [102.0, 0.5]
},
{
"type": "LineString",
"coordinates": [
[102.0, 0.0],
[103.0, 1.0],
[104.0, 0.0],
[105.0, 1.0]
]
}
]
}
There are some suggestions for GeometryCollection:
- Should not use nested GeometryCollection.
- Should not use GeometryCollection composed of a single part (use single part type instead) or a number of parts of a single type (use multipart type instead).
Antimeridian Cutting
Any geometry that crosses the antimeridian SHOULD be represented by cutting it in two such that neither part’s representation crosses the antimeridian. For example, if a Polygon across the antimeridian, it should be cutted in two and represented as a MultiPolygon.
Feature Object
A Feature object represents a spatially bounded thing. It has three members: type, geometry (do not confused with geometries in GeometryCollection) and properties:
{
"type": "Feature",
"geometry": {
"type": "LineString",
"coordinates": [
[102.0, 0.0],
[103.0, 1.0],
[104.0, 0.0],
[105.0, 1.0]
]
},
"properties": {
"prop0": "value0",
"prop1": 0.0
}
- The value of
typeis alwaysFeature. - The value of the
geometrymember SHALL be either a Geometry object as defined above or a JSON null value (in the case that the Feature is unlocated). - The value of the
propertiesmember is an object (any JSON object or a JSON null value).
If a Feature has a commonly used identifier, that identifier SHOULD be included as a member of the Feature object with the name id, and the value of this member is either a JSON string or number.
FeatureCollection Object
A FeatureCollection object has two members: type and features:
{
"type": "FeatureCollection",
"features": [{
"type": "Feature",
"geometry": {
"type": "Point",
"coordinates": [102.0, 0.5]
},
"properties": {
"prop0": "value0"
}
}]
}
- The value of
typeis alwaysFeatureCollection - The value of
featureis a JSON array. Each element of the array is a Feature object as defined above. It is possible for this array to be empty.
Bounding Box
A GeoJSON object MAY have a member named bbox to include information on the coordinate range for its Geometrys, Features, or FeatureCollections.
- The value of it MUST be an array of length 2*n, where n is the number of dimensions.
- From the southwesterly point to the more northeasterly point.
{
"type": "FeatureCollection",
"bbox": [100.0, 0.0, 105.0, 1.0],
"features": [
//...
]
}
TopoJSON
Reference: